Projects
What is Metal Part Fabrication? Techniques, Processes, and Applications Explained
Metal part fabrication is a cornerstone of the manufacturing industry, encompassing a variety of processes by which metal materials are transformed into functional components for numerous applications. According to a report by Allied Market Research, the global metal fabrication market was valued at approximately $17 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $24 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 5.1%. This surge underscores the increasing demand for complex metal parts in sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and construction, where precision and durability are critical.
The techniques involved in metal part fabrication range from traditional methods like welding and machining to advanced techniques such as laser cutting and additive manufacturing. These processes not only enhance design flexibility but also contribute to material efficiency and cost reduction. The versatility of metal part fabrication allows industries to innovate continuously, creating tailored solutions that meet specific requirements. As manufacturers navigate the dynamics of global supply chains and technological advancements, understanding the various fabrication methods and their applications becomes essential for maintaining competitive advantage in the rapidly evolving marketplace.

Overview of Metal Part Fabrication and Its Importance
Metal part fabrication is a pivotal process in manufacturing that involves transforming raw metal materials into specific components for various applications. This process encompasses a variety of techniques, including cutting, bending, welding, and machining, each tailored to create precise and efficient parts. The importance of metal part fabrication is evident across multiple industries, such as automotive, aerospace, and construction, where high-quality metal components are essential for the performance and safety of complex systems.
When engaging in metal part fabrication, it’s crucial to consider the selection of material based on the application’s requirements. Different metals offer unique properties that can affect factors like strength, weight, and corrosion resistance. For instance, stainless steel is favored for its durability in harsh environments, while aluminum is preferred for applications that require lightweight components.
Tips for successful metal fabrication include maintaining consistency in dimensions to ensure parts fit together seamlessly, and investing in advanced machinery to enhance precision. Additionally, frequent quality checks throughout the fabrication process can prevent costly errors and ensure that the final product meets stringent industry standards. By prioritizing these factors, manufacturers can improve efficiency and output, ultimately contributing to the advancement of technology and infrastructure.
Key Techniques Used in Metal Part Fabrication Processes
Metal part fabrication encompasses a diverse range of techniques aimed at transforming raw metal materials into functional components used across various industries. The key techniques in this process include machining, welding, bending, and forming, each serving its unique purpose and offering distinct advantages.
Machining is one of the most prevalent techniques employed in metal part fabrication, known for its precision. According to a market analysis report by Grand View Research, the global machining market size is projected to reach USD 212.5 billion by 2026, driven by the automotive and aerospace sectors that require high-quality, intricate components. Welding follows as a fundamental method that joins metals together, ensuring structural integrity. Processes such as MIG and TIG welding are favored for their versatility and ability to work with various metal types.
Bending and forming techniques, on the other hand, manipulate the material's shape through processes like press brake bending and roll forming. These methods are crucial in creating complex geometries needed in sheet metal fabrication. The global sheet metal market is expected to reach USD 334.1 billion by 2027, highlighting significant demand for these techniques in industries ranging from construction to electronics.
Tips: When selecting a fabrication technique, consider the intended application and material properties. Precision machining is ideal for high-tolerance parts, while welding is best for larger assemblies. Additionally, always consult with a skilled engineer to determine the most cost-effective and efficient fabrication method tailored to your project needs.
Detailed Description of Common Metal Fabrication Techniques
Metal fabrication involves a variety of techniques that transform raw metal materials into finished products. Among the most common methods are cutting, welding, bending, and machining—each serving distinct purposes in the fabrication process.
Cutting techniques include methods like shearing or laser cutting, which create precise edges and shapes for metal parts. Meanwhile, welding involves joining pieces together by melting and fusing them, making it essential for creating robust structures in everything from automotive to construction applications.
Bending is another vital technique that shapes metal into curves or angles, often using tools like press brakes to achieve the desired form. This process is crucial for creating components that fit specific design requirements, especially in industries such as HVAC and furniture manufacturing.
Finally, machining, which encompasses drilling, milling, and turning, trims and refines fabricated parts to achieve precise dimensions and surface finishes. Each of these techniques highlights the diverse methodologies involved in metal fabrication, showcasing how skilled craftsmanship and advanced technology work hand in hand to produce high-quality metal products for various applications.
Applications of Fabricated Metal Parts Across Various Industries
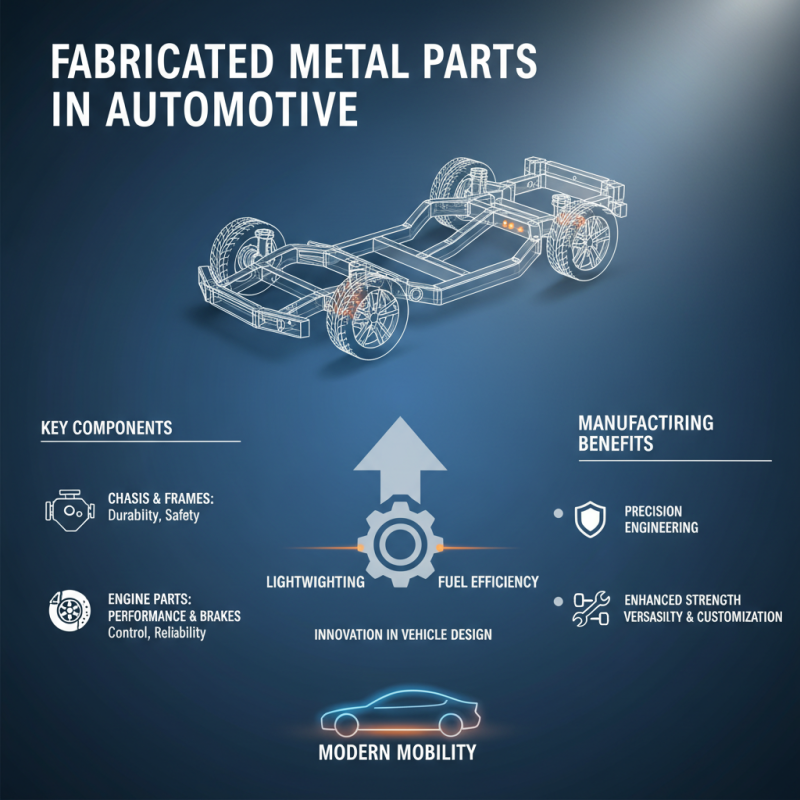
Fabricated metal parts play a crucial role across various industries, demonstrating their versatility and essential function in modern manufacturing. In the automotive industry, for instance, fabricated components are used extensively to create vehicles that are not only durable but also lightweight, enhancing fuel efficiency. From chassis and frames to engine parts, these metal components are crucial for ensuring the performance and safety of automobiles, showcasing how fabrication techniques contribute directly to innovation in vehicle design.
The aerospace sector also heavily relies on fabricated metal parts, where precision and reliability are paramount. Components such as brackets, supports, and wing structures must withstand extreme conditions while maintaining structural integrity. Advanced fabrication techniques, including laser cutting and CNC machining, are employed to meet the rigorous standards of this industry. Additionally, fabricated metal parts find applications in construction, where they are essential in forming structural supports and frameworks, aiding in building strong and resilient infrastructures. Each application highlights the critical role that metal fabrication plays in enhancing functionality and safety across diverse fields.
Future Trends and Innovations in Metal Part Fabrication
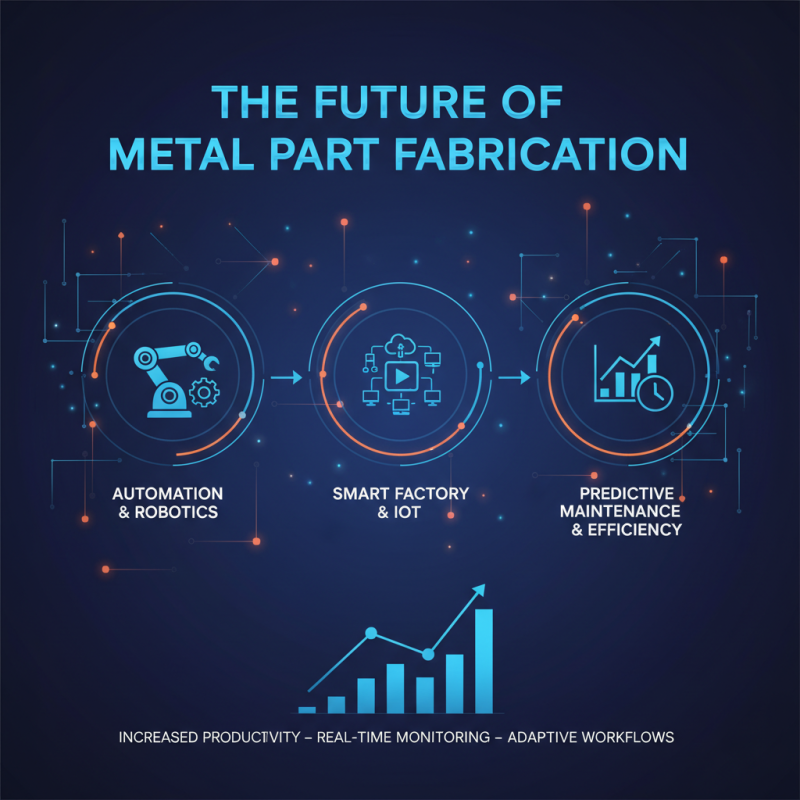
The future of metal part fabrication is driven by significant technological advances and innovations that are reshaping the industry. One of the most notable trends is the widespread adoption of automation and robotics, which enhances productivity and precision in manufacturing processes. As manufacturers incorporate smart technologies and the Internet of Things (IoT), they can monitor performance in real-time, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing downtime. This connectivity promotes a more efficient workflow, allowing for rapid adjustments based on data analysis and demand fluctuations.
Another emerging trend is the increasing use of additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing. This technique allows for the creation of complex geometries that traditional methods may struggle to achieve. As materials technology improves, more metal alloys are becoming compatible with additive processes, opening up new design possibilities and reducing material waste. Furthermore, sustainable practices are at the forefront, as companies look to minimize their environmental impact through recycling and the use of eco-friendly materials. These innovations not only enhance efficiency but also provide a competitive edge in a rapidly evolving market, setting the stage for a more sustainable and technologically advanced future in metal part fabrication.
Related Posts
-

Top 10 Important Factors to Consider in Iron Fabrication Projects
-

Top 10 Tips for Successful Online Sheet Metal Fabrication Projects
-

Top 10 Custom Stainless Fabrication Techniques for Your Next Project
-

How to Get Started with Welding and Fabrication Techniques for Beginners
-

10 Essential Tips for Successful Online Fabrication Projects
-

Why Welding and Fabrication Skills Are Essential for Modern Industries
